Predict the product for the following diels alder reaction – In the realm of organic chemistry, the Diels-Alder reaction stands as a cornerstone, a powerful tool for constructing complex molecules with remarkable precision. This analysis delves into the intricacies of this reaction, unraveling the mechanisms that govern its regio- and stereoselectivity, and empowering us to predict the products of specific Diels-Alder reactions with remarkable accuracy.
Introduction
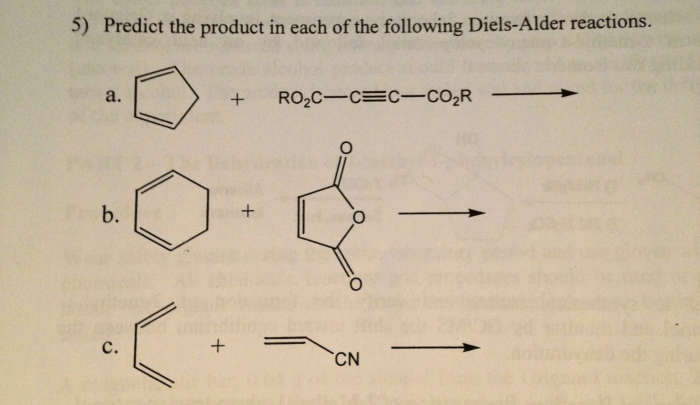
The Diels-Alder reaction is a powerful cycloaddition reaction that involves the addition of a conjugated diene to a dienophile, resulting in the formation of a cyclohexene ring. It is one of the most versatile and widely used reactions in organic chemistry, and has found numerous applications in the synthesis of complex molecules and natural products.The
purpose of this analysis is to provide a comprehensive overview of the Diels-Alder reaction, including its mechanism, regioselectivity, stereoselectivity, and applications. We will also discuss methods for predicting the product of a given Diels-Alder reaction.
Reaction Mechanism
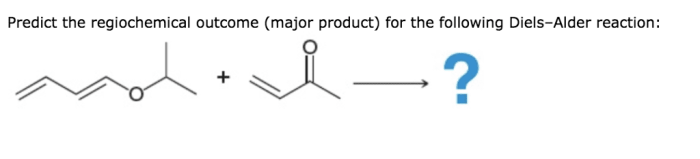
The Diels-Alder reaction proceeds through a concerted cycloaddition mechanism. The first step is the formation of a transition state, in which the diene and dienophile are oriented in a parallel fashion. The diene then undergoes a [4+2] cycloaddition with the dienophile, resulting in the formation of a cyclohexene ring.The
regioselectivity of the Diels-Alder reaction is determined by the relative reactivity of the diene and dienophile. The more reactive diene will add to the less reactive dienophile, and vice versa. The stereoselectivity of the reaction is determined by the orientation of the diene and dienophile in the transition state.
The endo product is formed when the diene and dienophile are oriented in a cis fashion, while the exo product is formed when they are oriented in a trans fashion.
Regioselectivity and Stereoselectivity
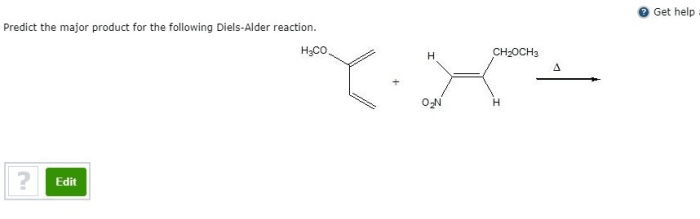
The regioselectivity and stereoselectivity of the Diels-Alder reaction can be influenced by a number of factors, including the substituents on the diene and dienophile, the temperature, and the solvent.Electron-withdrawing substituents on the diene will increase its reactivity, while electron-donating substituents will decrease its reactivity.
Electron-withdrawing substituents on the dienophile will decrease its reactivity, while electron-donating substituents will increase its reactivity.The temperature of the reaction will also affect the regioselectivity and stereoselectivity. Higher temperatures will favor the formation of the endo product, while lower temperatures will favor the formation of the exo product.The
solvent can also affect the regioselectivity and stereoselectivity of the reaction. Polar solvents will favor the formation of the endo product, while nonpolar solvents will favor the formation of the exo product.
Predicting the Product
There are a number of methods that can be used to predict the product of a given Diels-Alder reaction. One common method is to use the Woodward-Hoffmann rules. These rules state that the reaction will proceed with a concerted mechanism if the diene and dienophile have the same symmetry.Another
method for predicting the product of a Diels-Alder reaction is to use the Frontier Molecular Orbital (FMO) theory. This theory states that the reaction will proceed if the HOMO of the diene and the LUMO of the dienophile have the same symmetry.Finally,
the product of a Diels-Alder reaction can also be predicted using computational methods. These methods can be used to calculate the energy of the transition state and the product, and can provide valuable insights into the regioselectivity and stereoselectivity of the reaction.
Applications of the Diels-Alder Reaction: Predict The Product For The Following Diels Alder Reaction
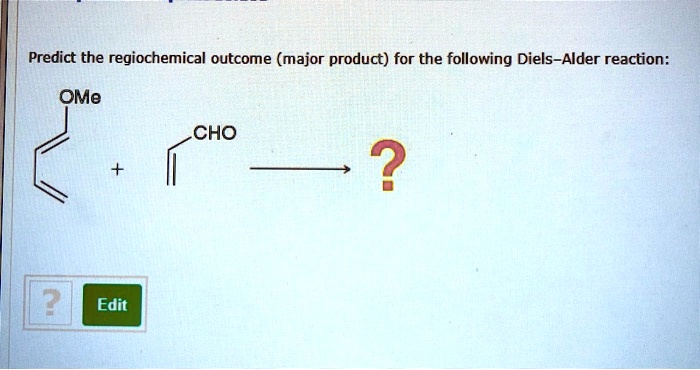
The Diels-Alder reaction is a versatile reaction that has found numerous applications in organic synthesis. It is used to synthesize a wide variety of complex molecules and natural products, including steroids, alkaloids, and terpenes.One of the most important applications of the Diels-Alder reaction is in the synthesis of steroids.
Steroids are a class of lipids that have a variety of biological functions, including regulating hormone levels and cholesterol metabolism. The Diels-Alder reaction is used to synthesize the steroid nucleus, which is the core structure of all steroids.The Diels-Alder reaction is also used to synthesize alkaloids.
Alkaloids are a class of nitrogen-containing compounds that have a variety of biological activities, including analgesic, anticonvulsant, and anticancer properties. The Diels-Alder reaction is used to synthesize the alkaloid nucleus, which is the core structure of all alkaloids.Finally, the Diels-Alder reaction is also used to synthesize terpenes.
Terpenes are a class of isoprenoids that have a variety of biological activities, including antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer properties. The Diels-Alder reaction is used to synthesize the terpene nucleus, which is the core structure of all terpenes.
Expert Answers
What is the Diels-Alder reaction?
The Diels-Alder reaction is a cycloaddition reaction between a conjugated diene and a dienophile, resulting in the formation of a cyclohexene ring.
What factors influence the regioselectivity of the Diels-Alder reaction?
The regioselectivity of the Diels-Alder reaction is influenced by the electronic properties of the diene and dienophile, as well as steric effects.
What is the role of temperature in the Diels-Alder reaction?
Temperature can affect the rate and selectivity of the Diels-Alder reaction, with higher temperatures generally favoring the formation of the endo product.