Electron configurations and orbital diagrams worksheet – Unveiling the intricacies of electron configurations and orbital diagrams, this comprehensive worksheet analysis embarks on a captivating journey into the fundamental building blocks of matter. By delving into the rules, principles, and applications of these concepts, we unravel the secrets of atomic structure and its profound implications in chemistry and beyond.
Through a meticulously crafted exploration, we decipher the intricacies of electron configurations, unraveling the patterns and periodic trends that govern the arrangement of electrons within atoms. We delve into the construction of orbital diagrams, visualizing the spatial distribution and orientations of electrons, providing a deeper understanding of their behavior and interactions.
Electron Configurations
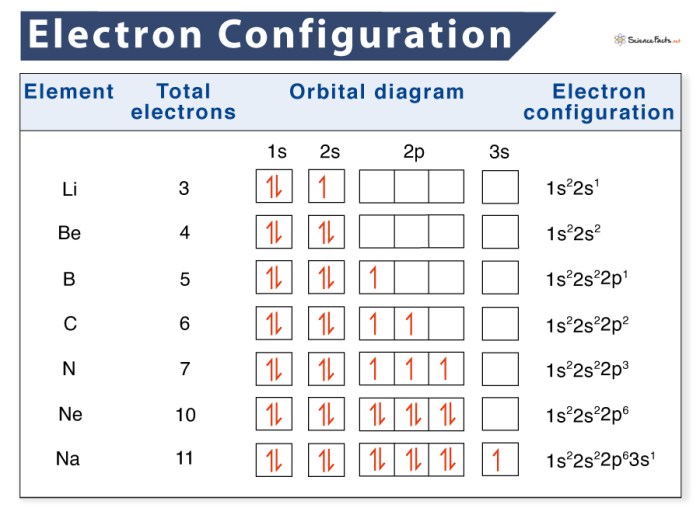
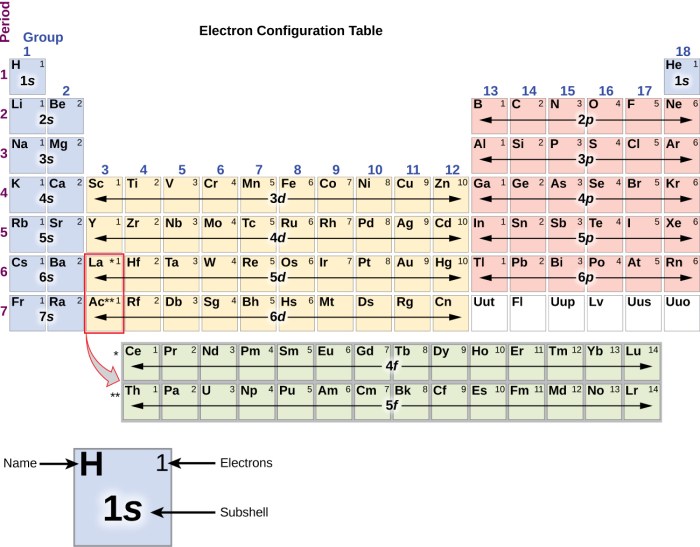
Electron configurations describe the distribution of electrons in an atom’s orbitals. They follow specific rules and principles, including the Pauli exclusion principle and Hund’s rule.
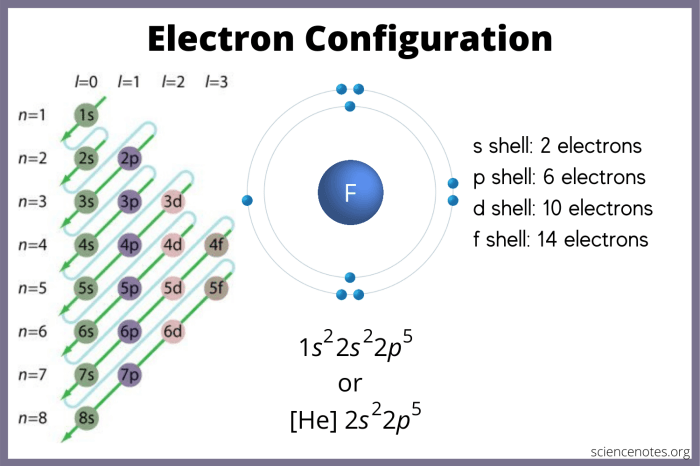
The electron configuration of an element indicates the number and arrangement of electrons in its atomic orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of helium (He) is 1s 2, meaning it has two electrons in the first energy level’s s-orbital.
Orbital Diagrams
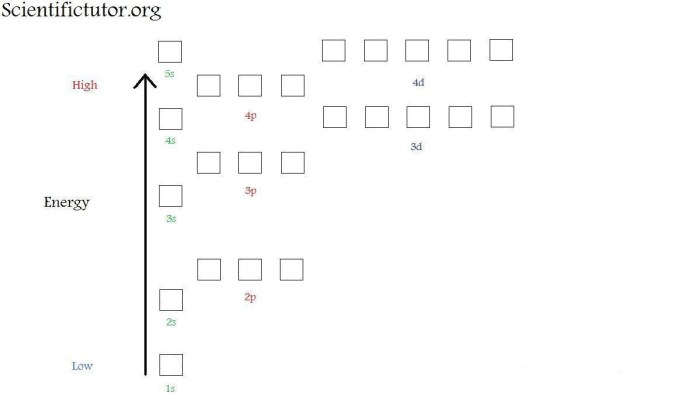
Orbital diagrams are visual representations of electron configurations. They show the shapes and orientations of atomic orbitals and the number of electrons in each orbital.
To construct an orbital diagram, determine the number of electrons in the atom and follow the Aufbau principle, which states that electrons fill orbitals in order of increasing energy.
Worksheet Analysis
The electron configurations and orbital diagrams worksheet covers key concepts such as electron distribution, orbital shapes, and energy levels.
It provides practice in writing electron configurations, drawing orbital diagrams, and understanding the relationship between electron configurations and atomic properties.
Areas for improvement could include expanding on advanced concepts like molecular orbital theory and providing more examples of real-world applications.
Applications and Examples, Electron configurations and orbital diagrams worksheet
Electron configurations and orbital diagrams are used in various fields, including chemistry and physics.
- In chemistry, they help explain chemical bonding, reactivity, and periodic trends.
- In physics, they contribute to understanding atomic structure, spectroscopy, and magnetism.
Advanced Concepts
Advanced concepts related to electron configurations and orbital diagrams include Hund’s rule, which describes the arrangement of electrons in orbitals with the same energy, and molecular orbital theory, which explains the bonding in molecules.
Hund’s rule states that electrons occupy orbitals with the same energy singly before pairing up, resulting in the maximum possible spin.
Molecular orbital theory describes the formation of molecular orbitals from the overlap of atomic orbitals, leading to the bonding and properties of molecules.
Popular Questions: Electron Configurations And Orbital Diagrams Worksheet
What is the significance of electron configurations?
Electron configurations provide crucial information about the stability, reactivity, and chemical properties of elements.
How do orbital diagrams contribute to our understanding of atomic structure?
Orbital diagrams offer a visual representation of electron distribution, enabling us to comprehend the shapes, orientations, and energy levels of atomic orbitals.
What are the key applications of electron configurations and orbital diagrams?
These concepts find widespread applications in fields such as chemistry, physics, and materials science, aiding in the prediction of chemical bonding, molecular properties, and electronic behavior.