Embark on a journey through the fascinating world of quadrilaterals with our comprehensive guide to Unit 6 Quadrilaterals Test Answers. This in-depth resource provides a thorough understanding of quadrilateral properties, classification, area, perimeter, angles, diagonals, and real-world applications. Dive into the captivating realm of geometry and unlock the secrets of these versatile shapes.
Prepare to conquer your test with confidence as we explore the intricacies of quadrilaterals, unravel their characteristics, and master the techniques for solving complex problems. Let us embark on this intellectual adventure together, where knowledge and clarity await at every turn.
Quadrilaterals Definitions and Properties
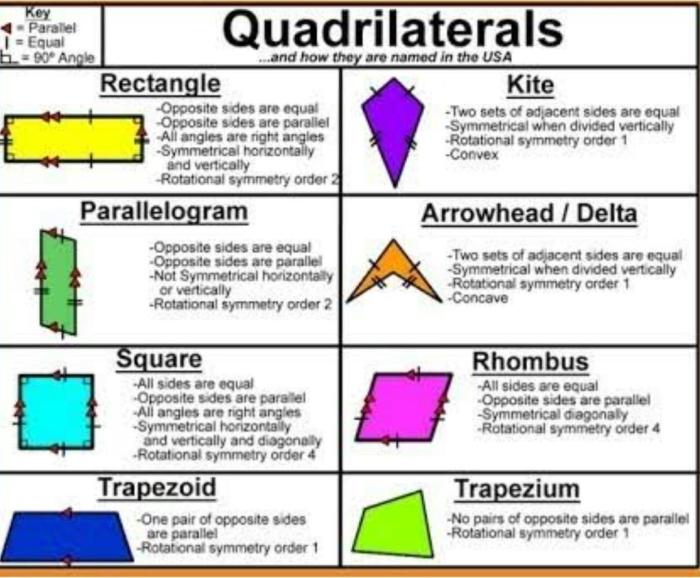
Quadrilaterals are two-dimensional shapes with four sides and four angles. They come in various types, each with its own unique set of properties.
Types of Quadrilaterals
- Square: A quadrilateral with all four sides of equal length and all four angles measuring 90 degrees.
- Rectangle: A quadrilateral with opposite sides of equal length and all four angles measuring 90 degrees.
- Parallelogram: A quadrilateral with opposite sides parallel and equal in length.
- Trapezoid: A quadrilateral with only one pair of parallel sides.
Key Properties, Unit 6 quadrilaterals test answers
- Sum of Interior Angles: The sum of the interior angles of a quadrilateral is always 360 degrees.
- Opposite Angles: The opposite angles of a quadrilateral are supplementary (add up to 180 degrees).
- Diagonals: The diagonals of a quadrilateral bisect each other.
Formulas and Theorems
- Area of a Square: A = s², where s is the length of a side.
- Area of a Rectangle: A = lw, where l is the length and w is the width.
- Area of a Parallelogram: A = bh, where b is the base and h is the height.
- Area of a Trapezoid: A = (b₁ + b₂)h/2, where b₁ and b₂ are the lengths of the parallel bases and h is the height.
Identifying and Classifying Quadrilaterals: Unit 6 Quadrilaterals Test Answers
Quadrilaterals can be identified and classified based on their properties.
Methods of Identification
- Side Lengths: Equal or unequal side lengths.
- Angle Measures: 90-degree angles, supplementary angles, etc.
- Parallel Sides: Opposite sides parallel or not.
Classification Table
| Property | Square | Rectangle | Parallelogram | Trapezoid |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equal Sides | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| 90-degree Angles | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Parallel Sides | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes (only one pair) |
Area and Perimeter of Quadrilaterals
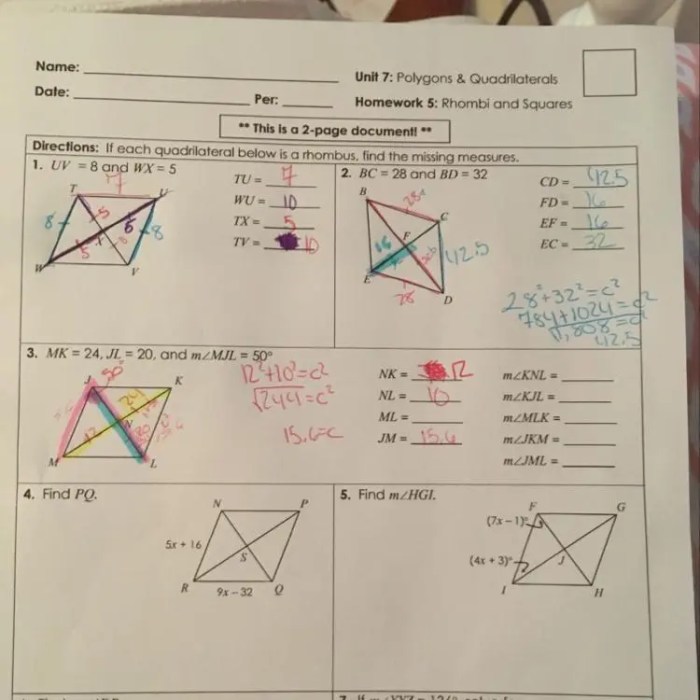
The area and perimeter of quadrilaterals can be calculated using specific formulas.
Area Formulas
- Square: A = s², where s is the length of a side.
- Rectangle: A = lw, where l is the length and w is the width.
- Parallelogram: A = bh, where b is the base and h is the height.
- Trapezoid: A = (b₁ + b₂)h/2, where b₁ and b₂ are the lengths of the parallel bases and h is the height.
Perimeter Formulas
- Square: P = 4s, where s is the length of a side.
- Rectangle: P = 2(l + w), where l is the length and w is the width.
- Parallelogram: P = 2(b + h), where b is the base and h is the height.
- Trapezoid: P = b₁ + b₂ + l₁, where b₁ and b₂ are the lengths of the parallel bases and l₁ is the length of the non-parallel side.
Step-by-Step Calculations
- Identify the type of quadrilateral.
- Measure or find the relevant side lengths, heights, and angles.
- Substitute the values into the appropriate formula.
- Calculate the area or perimeter.
Angles and Diagonals of Quadrilaterals
The angles and diagonals of quadrilaterals have specific relationships.
Angle Properties
- Sum of Interior Angles: 360 degrees.
- Opposite Angles: Supplementary (add up to 180 degrees).
Diagonal Properties
- Diagonals Bisect Each Other: The diagonals of a quadrilateral bisect each other.
- Diagonals in Parallelograms: Divide the parallelogram into four congruent triangles.
Applications of Quadrilaterals
Quadrilaterals are widely used in various fields.
Architecture
- Building foundations
- Window and door frames
- Roof designs
Engineering
- Bridges
- Machinery
- Transportation
Design
- Furniture
- Artwork
- Logos and symbols
Importance of Understanding Quadrilateral Properties
- Ensures structural stability in architecture and engineering.
- Facilitates efficient design and aesthetics.
- Enables accurate calculations and measurements.
Essential FAQs
What is the formula for calculating the area of a rectangle?
Area = length x width
How do I classify a quadrilateral based on its properties?
Use the properties of angles, sides, and diagonals to identify the specific type of quadrilateral (e.g., square, rectangle, parallelogram, trapezoid).
What is the relationship between the diagonals of a parallelogram?
The diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other.